OS Basic
The followings are decribed based on IA-64 Linux system.
Machine Level
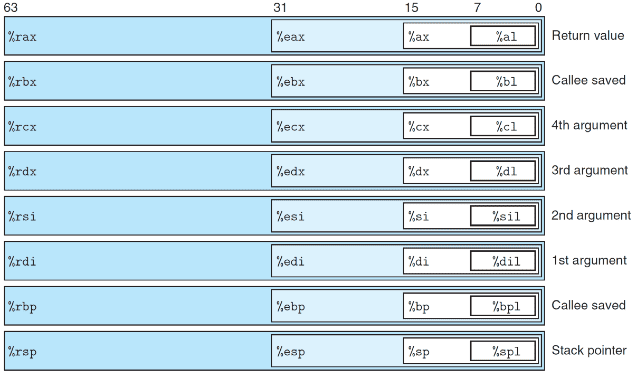
Regs in IA-64
- 16 integer register (8-byte long)
- %rax, %rcx, %rdx, %rbx, %rsi, %rdi, %rsp, %rbp
- %r8, %r9, %r10, %r11, %r12, %13, %r14, %r15
Note: %rsp only points to stack top
- 16 floating point register (32-byte long)
Instruction
No instruction can load two address together
- push
S(add the value in registerSinto the stack)- R[%rsp] ← R[%rsp] - 8
- M[R[%rsp]] ← S
- pop D (pop the value from the stack top)
- D ← M[R[%rsp]]
- R[%rsp] ← R[%rsp]+8
- jmp change the %rip (used for if,for,loop)
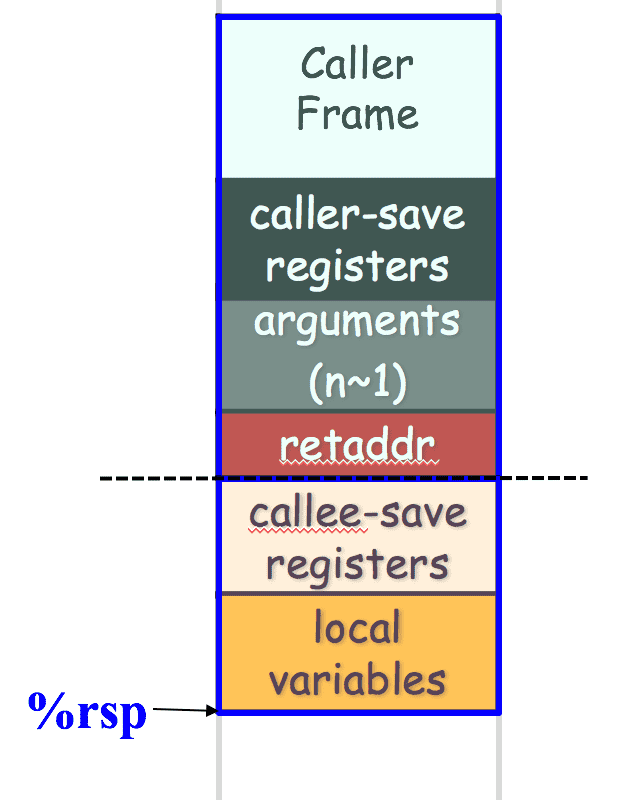
- call = push + jmp
- push caller-registers
- push arugments
- push retaddr (%rip, the address of next instruction)
hardware - jmp to callee address
by hardware
- ret
- restore callee-save registers(include %rbp)
- pop return address from the stack
hardware - jmp to the return address
hardware
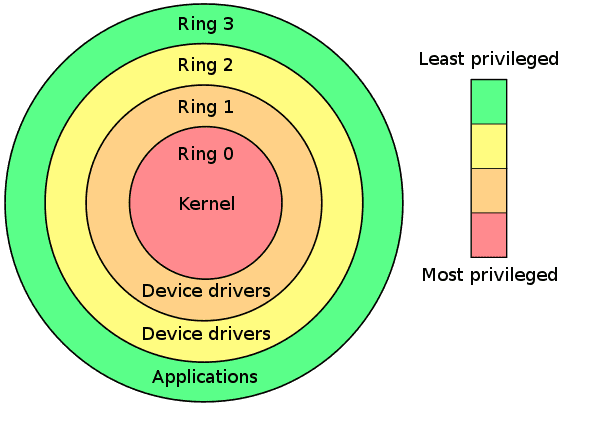
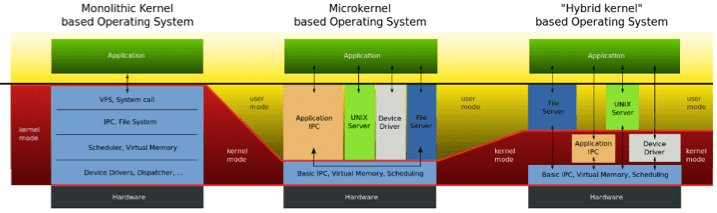
Kernel
Def: a shared chunk of OS code
- not a small process, but a part of some user process
Effect: typically use a mode bit to restrict an app on
- executing some privileged instrunctions
- access kernel address space
Mode Switch
- user -> kernel
- only when exception occurs and control passes to exception handler
- kernel -> user
- when control returns to the user code
Context Switches
- kernel maintains the states for kernel to restart a preempted process including
- value of PC
- register file
- status registers
- user stack
- kernel stack
- kernel data status
- process table
- page table
- filetable
- …
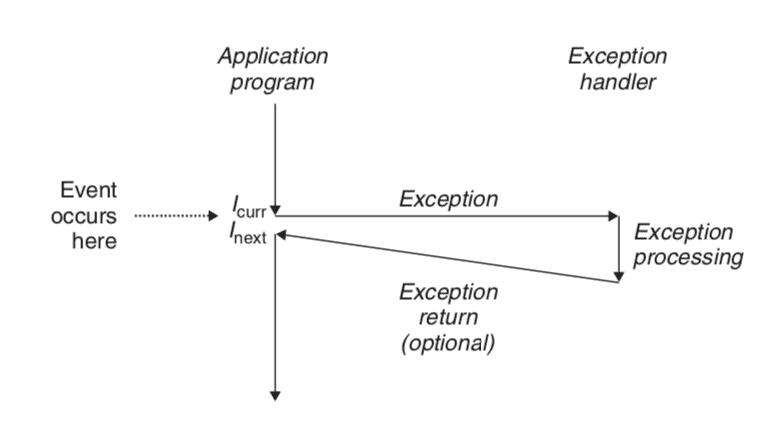
Excepetional Control Flow
- mechanism
- low level:
- exceptions (implemented by hardware and OS software)
- high level:
- e.g.
- process context switch (implemented by OS software)
- signals (implemented by OS software)
- nolocal jump (long jump, by C language runtime laibrary)
- e.g.
- low level:
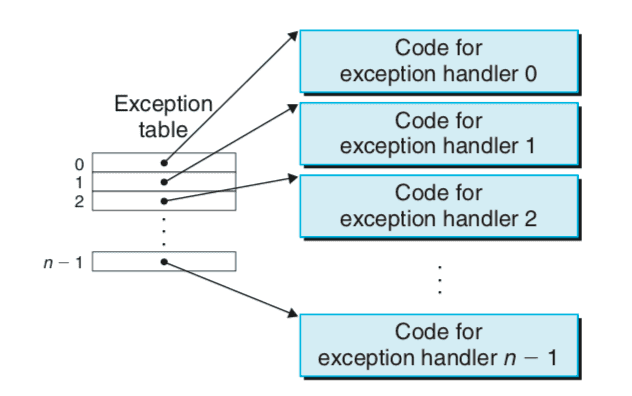
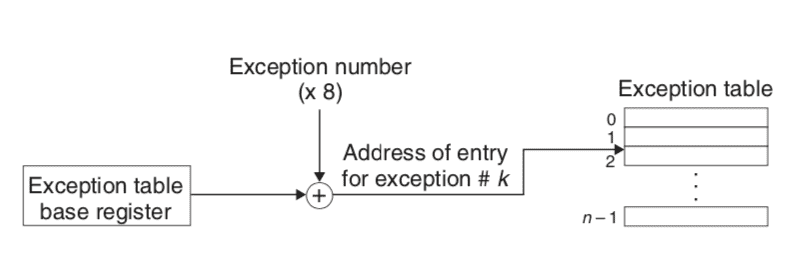
- handle exception process
- exception table
- exception classes
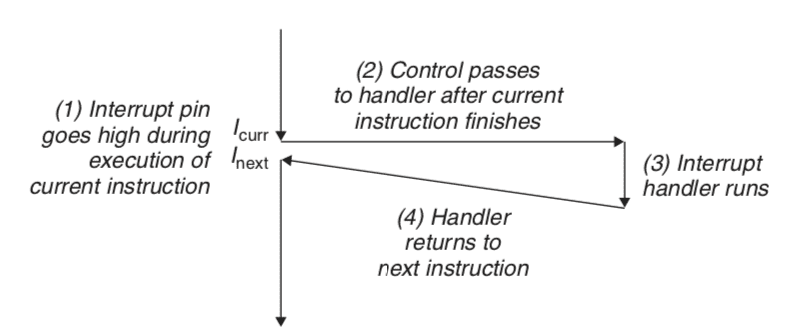
Interrupt - Signal from I/O device - Async - Always returns to next instruction
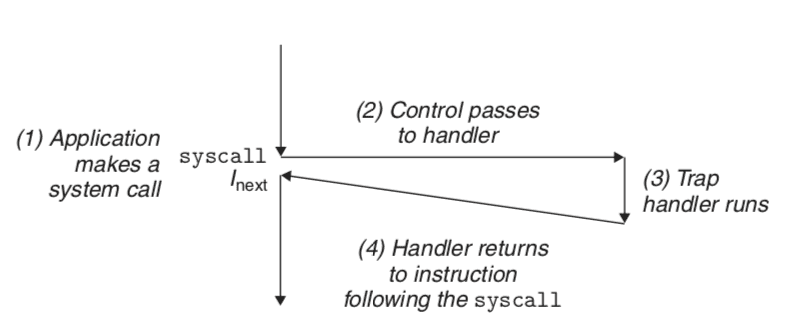
Trap - Intentional exception - Sync - Always returns to next instructio
Fault - Potentially recoverable error - Sync - Might return to current instruction
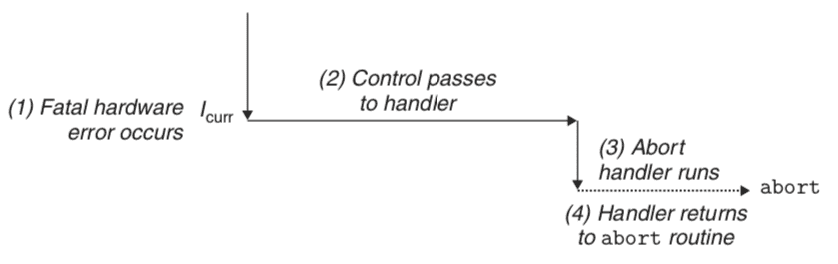
Abort - Nonrecoverable error - Sync - Never returns
memory
Order
主机序(Host Order)就是遵循Little-Endian规则.所以当两台主机之间要通过TCP/IP协议进行通信的时候就需要调用相应的函数进行主机序(Little-Endian)和网络序(Big-Endian)的转换
- XX-Endian是指原内容中XX部分在尾部地址存储
- Little-Endian: easy to cast, does not need to change address
- Big-Endian:easy to compute the decimal value, in line with human intuition
- e.g. 0x12345678
- little endian (Intel)
内存地址 0x4000 0x4001 0x4002 0x4003 存放内容 0x78 0x56 0x34 0x12 - big endian (Sum,IBM,network)
内存地址 0x4000 0x4001 0x4002 0x4003 存放内容 0x12 0x34 0x56 0x78
- little endian (Intel)
- check code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10int IsCPULittleEndian()
{
union
{
unsigned int i;
unsigned char c;
}u;
u.i = 1;
return (u.c == 1);
}
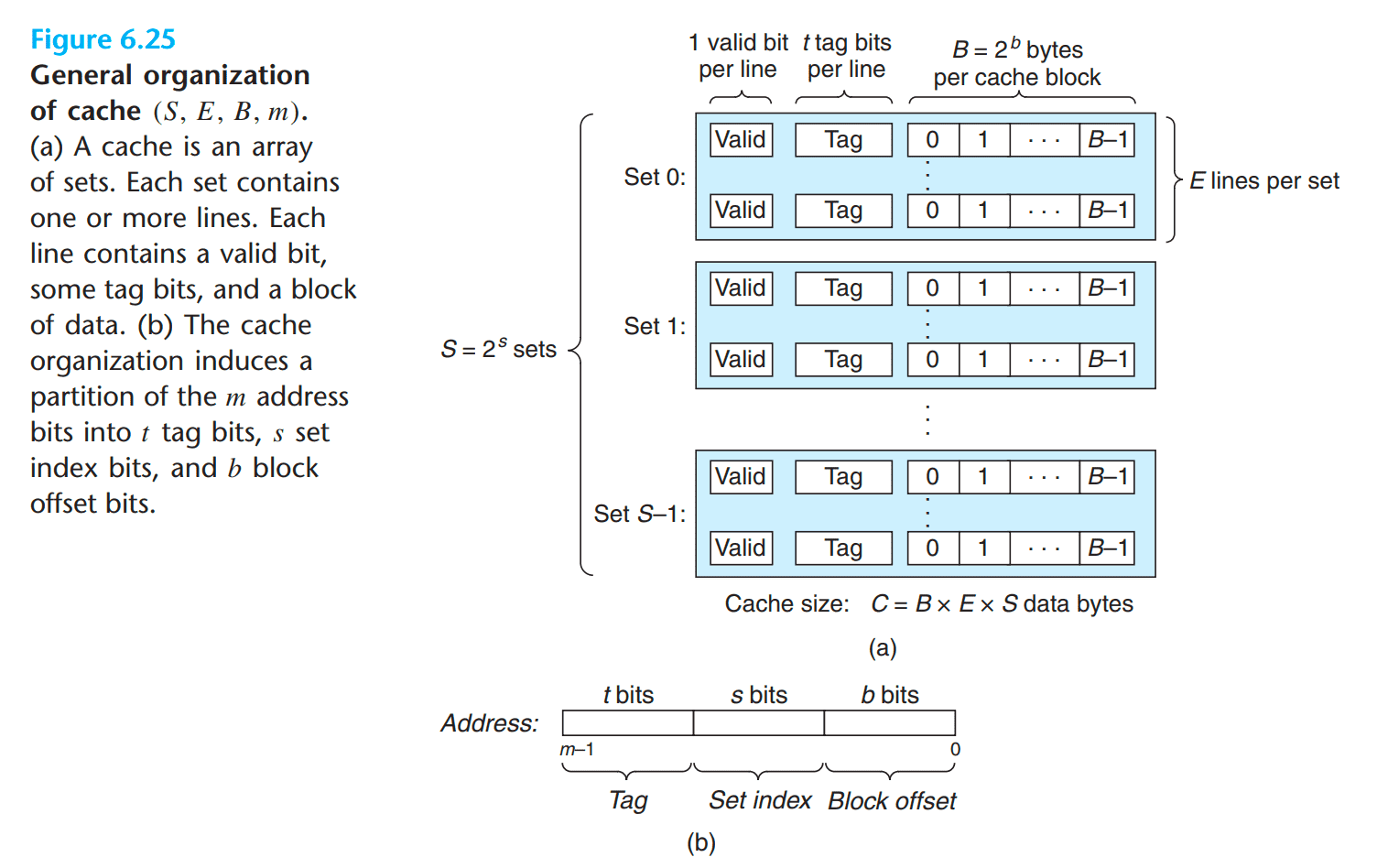
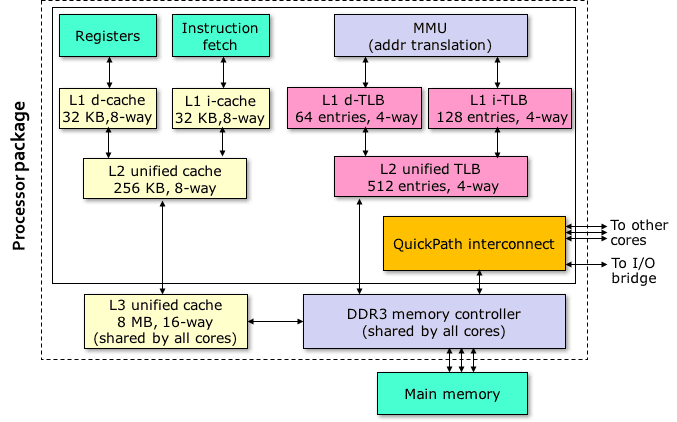
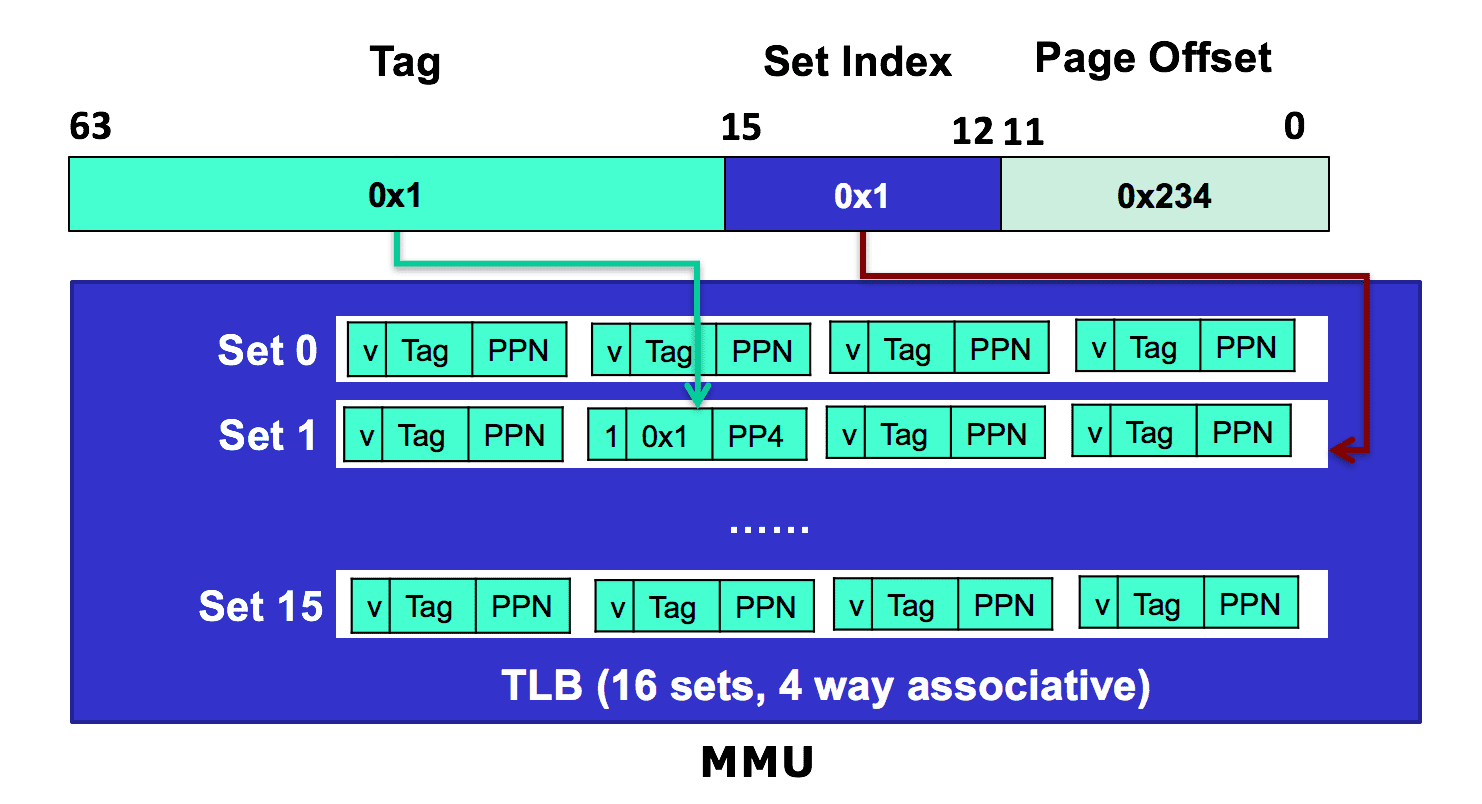
Physical Cache
we take the set associative cache as an example.
- parameters
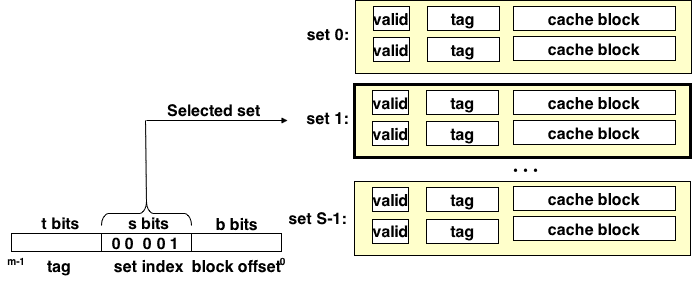
- set selection
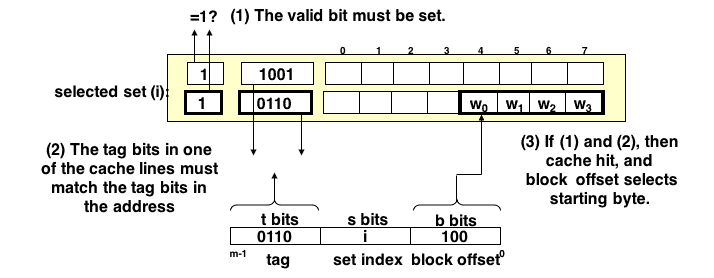
- must compare the tag in each valid line in the selected set.
Core i7 Structre
Cache Coherency
- Snooping Solution
- Send all requests for data to all processors
- Works well with bus (natural broadcast medium)
- Directory-Based Schemes
- Keep track of what is being shared in one centralized place
- Scales better than Snoop
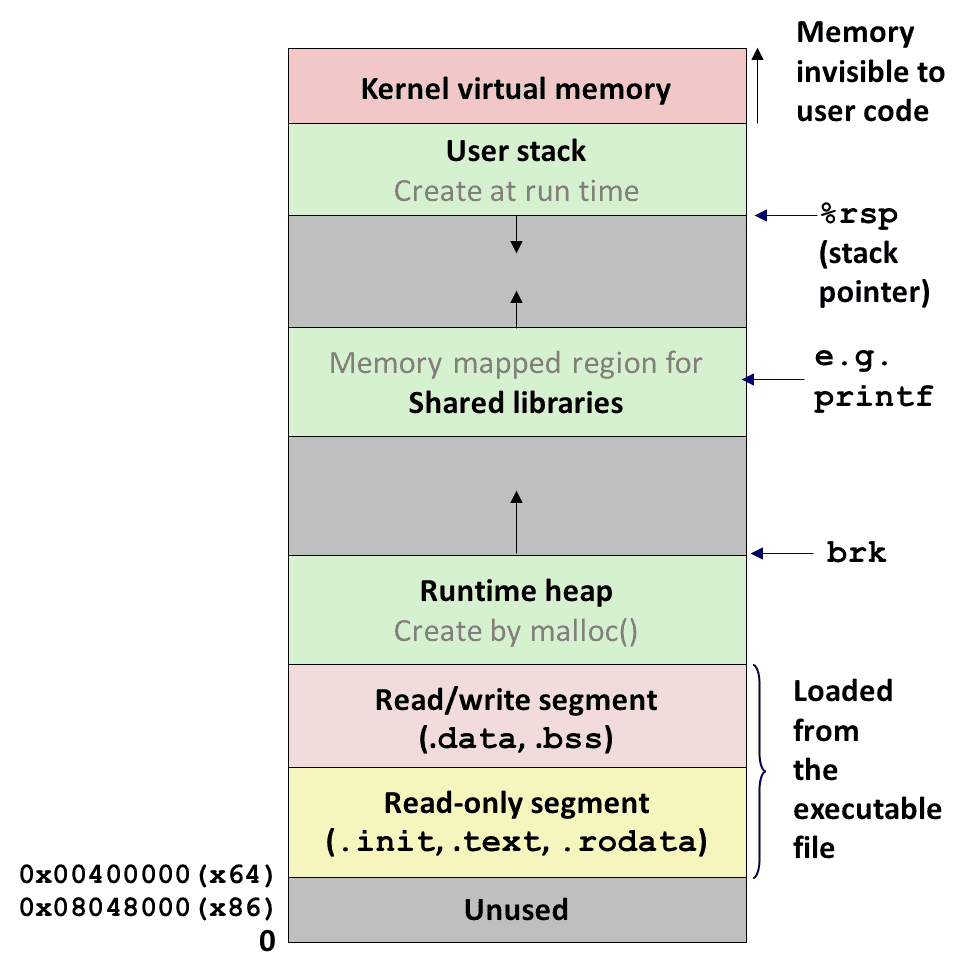
virtual memory hierarchy
- read-write (global)
- .data(initialized global variable)
- .bss(uninitialized global variabel)
- read only data
- e.g. constant, const string,
- read only code(below the data)
- machine code of the compiled program
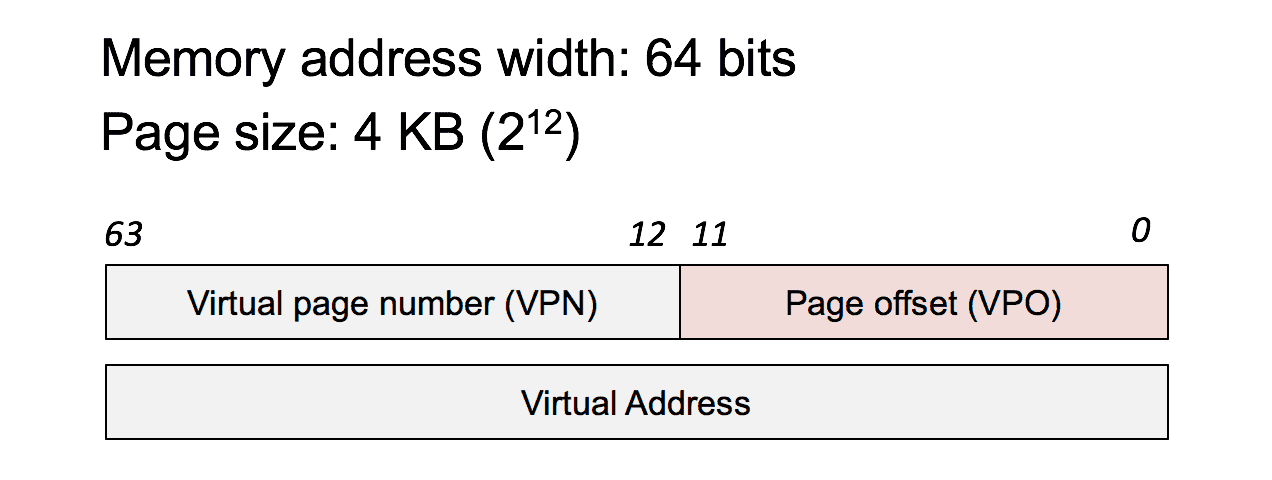
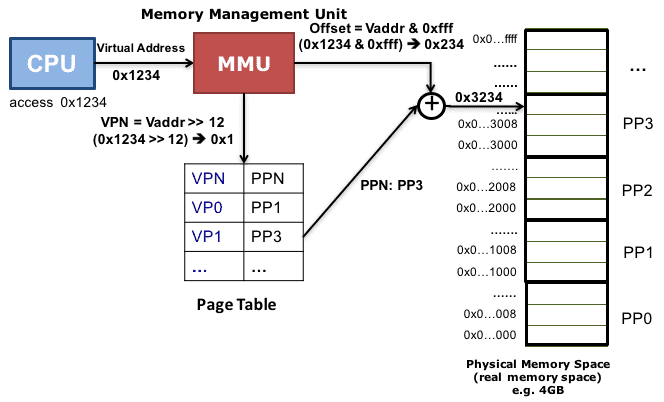
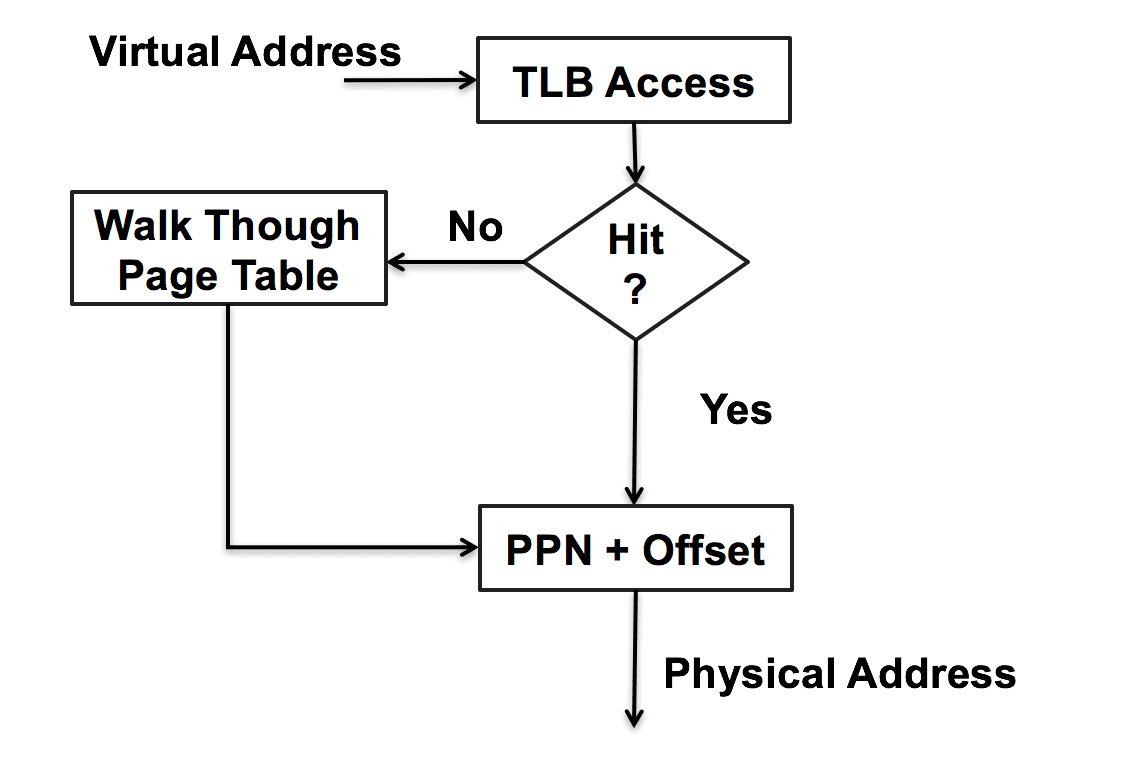
VA to PA
- VA
- MMU (memory management unit in CPU)
- multi level(64 support 4 level)
page table
- kernel maintian a page table for each process
- CR3 points to page table
- mapping from virtual pages to physical address(memory or disk)
- store in physical memory
TLB
- inside MMU
- a cache for page table
- to skip page table work through if TLB hit
- structure like Physical Cache
PAGE FAULT SEGMENTATION FAULT
- MMU generates “page fault”, if the physical page is in disk
- handled by OS
- use DMA load to memeory and change associate pointer of page table
- and then load from memory
- or access some memory can not access or not exist
OS aborts process with “segmentation fault”
Cache Algorithm
- FIFO
- link list
- LRU
- link list
- LFU
- min-heap
- Clock
- ring queue
- Hit:通过hash快速定位,并将reference bit设置为1
- Miss:
- 从Head开始查找Reference bit为0 的entry
- 如果Reference bit为1,清除该位,指针前移,直到找到为0的entry为止。
- 如果Reference bit 为0, 将数据放入该entry,并将Reference bit置1。
- these methods could add a hash table to quick check cahce hit but cost more space
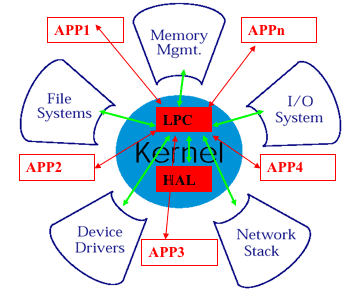
Kernel
- exokernel
Kernel: only protect the resources
Application: manage the resources
Reference
-《Introduction to Computer System》
All articles in this blog are licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 unless stating additionally.
Comment