线段树
线段树
适用场景
固定范围内区间统计,统计只能是可以合并的操作如:最值、求和
树状数组
在认识线段树之前,有个熟悉的结构,每一层分布跟归并排序过程类似,就是树状数组,如下:
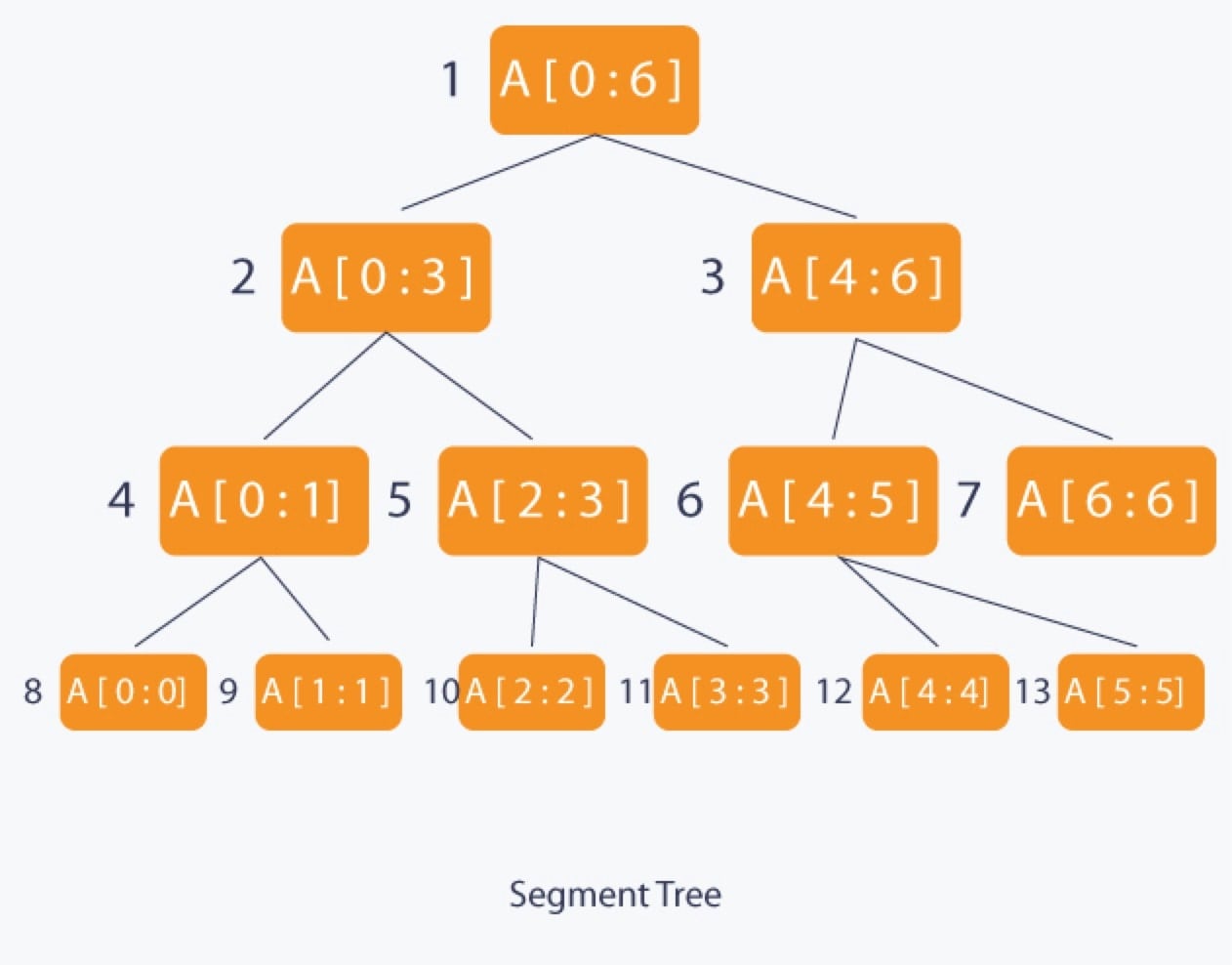
- T的根结点代表整个数组所在的区间对应的信息,及arr[0:N](不含N)所对应的信息。
- T的每一个叶结点存储对应于输入数组的每一个单个元素构成的区间arr[i]所对应的信息,此处0≤i<N。
- T的每一个中间结点存储对应于输入数组某一区间arr[i:j]对应的信息,此处0≤i<j<N。
其本质思想是分而治之。
代码详解
以如下问题为例来描述样例代码:
我们有一个长度为n的int数组,即A[0..n-1]
需要支持以下几种操作:
- 找到区间[l..r]内的元素之和
- 对区间[l..r]内的所有元素都更新为一个新的值x,即a[l..r]=x
理论也可以用链表实现,但是实际效率比如直接用数组实现慢许多。
构建 O(N)
可能有些人会当成N次更新,但是实际可以通过从树状数组尾部遍历来优化
- 递归版
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18void build(int node, int start, int end)
{
if(start == end)
{
// Leaf node will have a single element
tree[node] = A[start];
}
else
{
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
// Recurse on the left child
build(2*node, start, mid);
// Recurse on the right child
build(2*node+1, mid+1, end);
// Internal node will have the sum of both of its children
tree[node] = tree[2*node] + tree[2*node+1];
}
} - 高效版
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11// function to build the tree
void build( int arr[])
{
// insert leaf nodes in tree
for (int i=0; i<n; i++)
tree[n+i] = arr[i];
// build the tree by calculating parents
for (int i = n - 1; i > 0; --i)
tree[i] = tree[i<<1] + tree[i<<1 | 1];
}
查找 O(logN)
- 递归版
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18int query(int node, int start, int end, int l, int r)
{
if(r < start or end < l)
{
// range represented by a node is completely outside the given range
return 0;
}
if(l <= start and end <= r)
{
// range represented by a node is completely inside the given range
return tree[node];
}
// range represented by a node is partially inside and partially outside the given range
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
int p1 = query(2*node, start, mid, l, r);
int p2 = query(2*node+1, mid+1, end, l, r);
return (p1 + p2);
} - 高效版
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14// function to get sum on interval [l, r)
int query(int l, int r)
{
int res = 0;
// loop to find the sum in the range
for (l += n, r += n; l < r; l >>= 1, r >>= 1)
{
if (l&1)
res += tree[l++];
if (r&1)
res += tree[--r];
}
return res;
}
更新 O(logN)
递归版
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25void update(int node, int start, int end, int idx, int val)
{
if(start == end)
{
// Leaf node
A[idx] += val;
tree[node] += val;
}
else
{
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if(start <= idx and idx <= mid)
{
// If idx is in the left child, recurse on the left child
update(2*node, start, mid, idx, val);
}
else
{
// if idx is in the right child, recurse on the right child
update(2*node+1, mid+1, end, idx, val);
}
// Internal node will have the sum of both of its children
tree[node] = tree[2*node] + tree[2*node+1];
}
}高效版
如果是更新一个区间,那么就必须使用类似上面的递归分治过程。
如果是只更新一个元素,那可以用如下方法。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11// function to update a tree node
void updateTreeNode(int p, int value)
{
// set value at position p
tree[p+n] = value;
p = p+n;
// move upward and update parents
for (int i=p; i > 1; i >>= 1)
tree[i>>1] = tree[i] + tree[i^1];
}
二维线段树
即矩阵(假设N行M列)下的线段树,应对矩形区间内的更新和查询,有三种实现方法
- 基础的方法: 每一行当成一个一维线段树,那么更新和查询复杂度变成O(NlogM)
- 四分树: 即每次递归向下时分成四份 更新和查询复杂度变成(logM * logN)
- 分段线段树: 本质同四分树,时间复杂度也相同。 但是代码相对简单些。每次递归向下也是二分,只是对行二分和对列二分间隔进行(类似KD树),比如深度为偶数时对行二分,深度为奇数时对列二分。
小试牛刀
二维线段树 POJ2155
https://vjudge.net/contest/225622#problem/A
Reference
线段树(segment tree),看这一篇就够了
Segment Trees from hackerearth
Segment tree | Efficient implementation
二维线段树
All articles in this blog are licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 unless stating additionally.
Comment